The Role of a Content Engineer: Tools, Techniques, and the Art of Structured Content
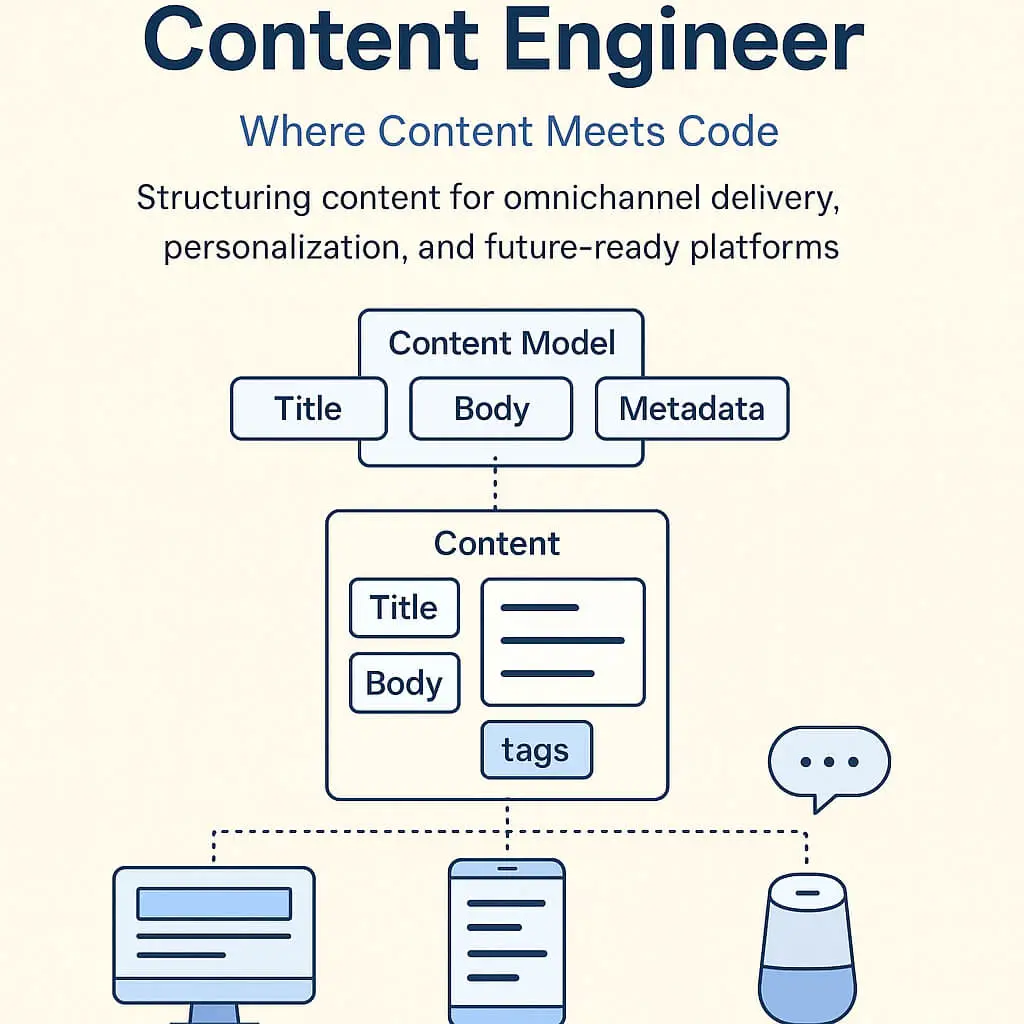
In today’s digital ecosystem, content is more than just words on a webpage — it’s a structured, intelligent asset that powers user experiences, automation, and personalization across platforms. Behind the scenes, Content Engineers play a critical role in designing, modeling, and optimizing this content so it can be reused, delivered, and understood across channels.
So, who exactly is a Content Engineer, what tools do they use, and how do they work?
What is a Content Engineer?
A Content Engineer sits at the intersection of content strategy, user experience, and technical infrastructure. Unlike content writers or copywriters, content engineers focus on structuring, tagging, modeling, and delivering content — not just writing it.
They ensure that content is:
- Reusable across platforms (web, mobile, apps, voice interfaces)
- Adaptable to different audiences and regions
- Structured in a way machines and humans can both understand
- Personalizable and ready for automation through AI/ML
Responsibilities of a Content Engineer
- Content modeling: Defining the types of content and their relationships (e.g., blog post, product page, FAQ).
- Content structure & schema: Building schemas (using JSON, XML, etc.) to ensure consistency and adaptability.
- Metadata & taxonomy: Designing tagging systems and metadata rules for better content discovery.
- Tool & CMS integration: Working with headless CMS tools and APIs to connect content with front-end applications.
- Collaboration: Partnering with developers, UX designers, content strategists, and SEO specialists.
Tools Used by Content Engineers
A successful content engineer has a solid technical toolkit. Here are some of the most commonly used tools and platforms:
1. Content Management Systems (CMS)
- Headless CMSs: Contentful, Sanity, Strapi, Prismic
- Traditional CMSs (for hybrid use): Drupal, WordPress (with REST APIs)
2. Schema and Modeling Tools
- JSON Schema, XML Schema, OpenAPI (for designing data formats and APIs)
- GraphQL (for querying structured content)
3. Version Control & Collaboration
- Git, GitHub, GitLab (for tracking content model changes)
- Jira, Confluence (project documentation and collaboration)
4. Content Design and Prototyping
- Figma, Adobe XD (for working with UX teams)
- Notion, Miro (for collaborative content planning)
5. Testing and Validation
- Content linting tools like Vale
- Accessibility testing: Axe, Lighthouse
6. APIs & Delivery
- RESTful APIs
- CDN integration (Cloudflare, Fastly)
- Static site generators: Next.js, Gatsby (to render structured content)
How Does a Content Engineer Write?
While Content Engineers aren’t always writing customer-facing copy, they do write structured content, documentation, and metadata. Their writing needs to be:
- Modular: Small pieces that can be reused across contexts (think LEGO blocks).
- Semantic: Clearly labeled using tags or schema.org definitions.
- Accessible: Optimized for screen readers, multilingual support, and mobile usability.
- Optimized: Structured for SEO, with metadata and meaningful hierarchy.
Example:
jsonCopyEdit{
"title": "How to Brew Coffee",
"author": "John Doe",
"tags": ["coffee", "brewing", "tutorial"],
"body": {
"intro": "Brewing the perfect cup of coffee is both a science and an art.",
"steps": [
"Boil water to 96°C",
"Grind beans to medium-coarse",
"Pour over slowly",
"Enjoy"
]
}
}
Content Engineering vs. Content Strategy vs. UX Writing
| Role | Focus |
|---|---|
| Content Engineer | Content structure, delivery, schema, and systems |
| Content Strategist | Governance, workflows, editorial strategy |
| UX Writer | Microcopy, UI text, tone & voice |
They all work together, but content engineers are the bridge between content and code.
Why Are Content Engineers So Important?
- Omnichannel Delivery: They ensure your content works on web, mobile, smart speakers, chatbots, etc.
- Scalability: Structured content is easier to translate, personalize, and scale.
- AI-Readiness: AI tools like ChatGPT, voice assistants, and chatbots depend on clean, structured, and semantic content.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Well-modeled content enables agile development and reduces redundancies.
Final Thoughts
In a world of ever-evolving digital channels, Content Engineers are the unsung heroes enabling consistency, efficiency, and innovation. Their work helps organizations deliver the right message, to the right person, at the right time — regardless of platform.
If you’re building a digital product, launching a multi-language site, or integrating with AI tools, don’t overlook the power of content engineering. It’s not just about what you say — it’s about how well you’ve structured it to be said everywhere.